Stray Light Information
Stray light is exhibited when wavelengths other than those selected appear at the measurement plane. It is generally caused by diffraction, light scattering from imperfections on the grating surface or ghost orders (eg periodic errors in the spacing of ruled gratings) that cause wavelengths to follow unintended paths within an optical system.
The effect of stray light is to give an apparent higher signal level at any given wavelength and negatively impact the signal to noise ratio (SNR).
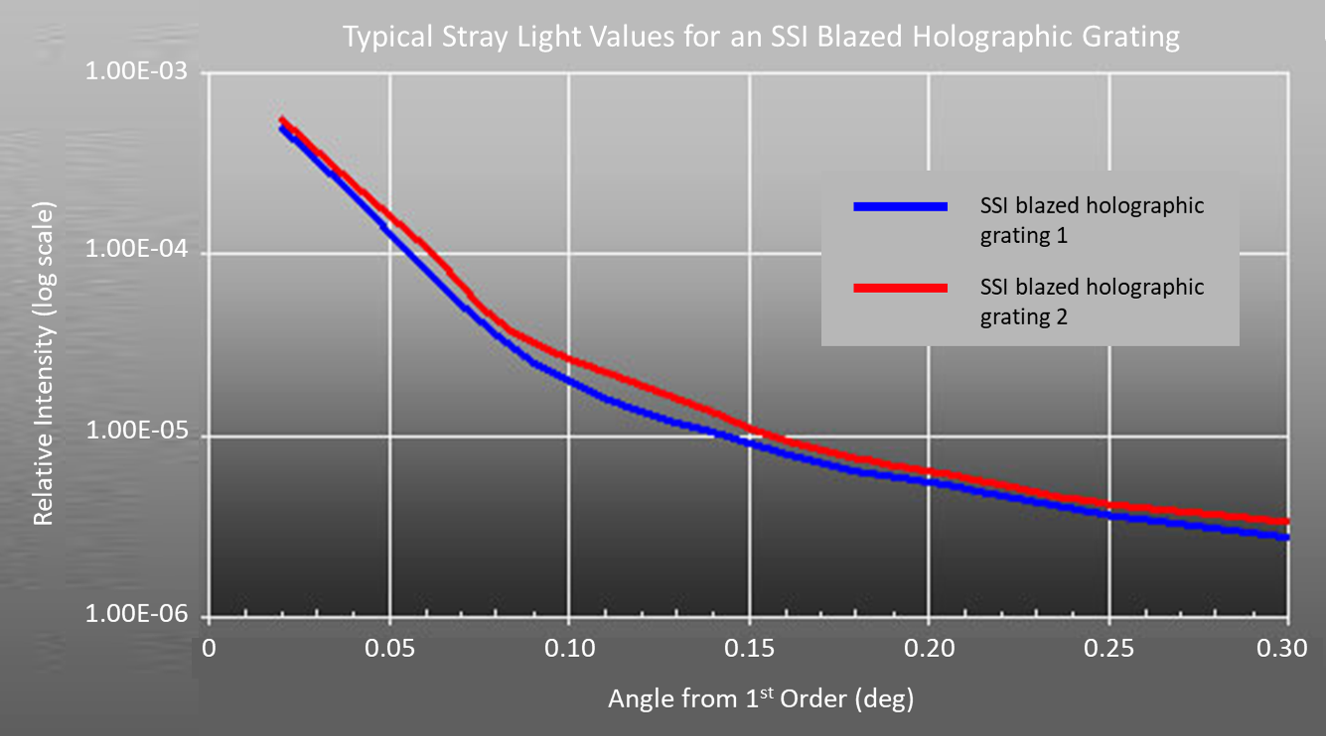
Stray light levels for SSI 2880g/mm, 325nm Blazed Holographic Grating, log scale.
Spectrum Scientific utilizes a proprietary blazing technique that significantly reduces stray light in diffraction gratings, especially when compared to ion etched blazed holographic gratings. For a comparison, please click here.